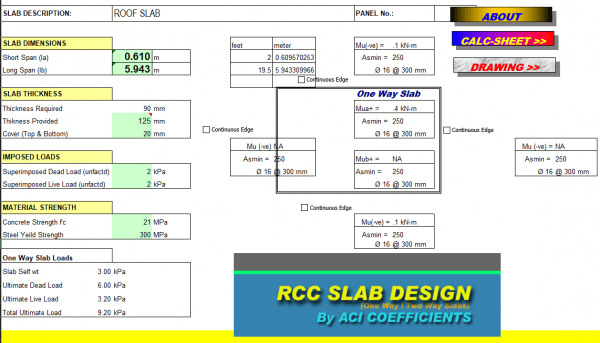
The coefficient method may be the simplest, easiest and the quickest approach for the design of two–way slab supported by edge beam on all slab sides. This method was provided in the American Concrete Institute (ACI) in 1963 to design two–way slabs carried by steel beams, deep beam, or walls.
A concrete slab is a common structural element of modern buildings, consisting of a flat, horizontal surface made of cast concrete. Steel-reinforced slabs, typically between 100 and 500 mm thick, are most often used to construct floors and ceilings, while thinner mud slabs may be used for exterior paving (see below).
In many domestic and industrial buildings, a thick concrete slab supported on foundations or directly on the subsoil, is used to construct the ground floor. These slabs are generally classified as ground-bearing or suspended. A slab is ground-bearing if it rests directly on the foundation, otherwise the slab is suspended. For multi-storey buildings, there are several common slab designs
While inputting the data for designing, use input sheet and for results see result sheet


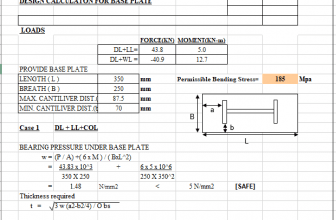
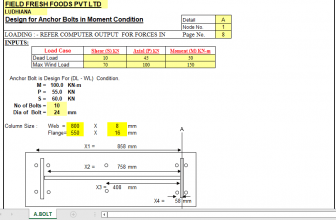

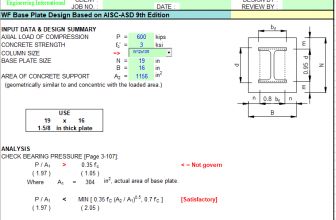
thank you
Dear Admin,
Please update the link.
Thank you.
Dear, link updated , please check
Dear Admin,
Please update the download link.
Thank you.
Dear, link updated , please check