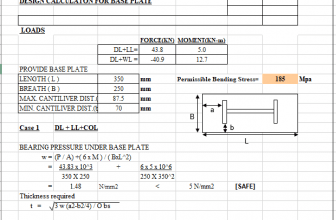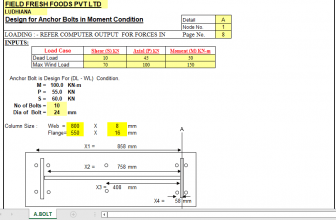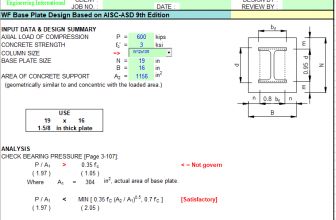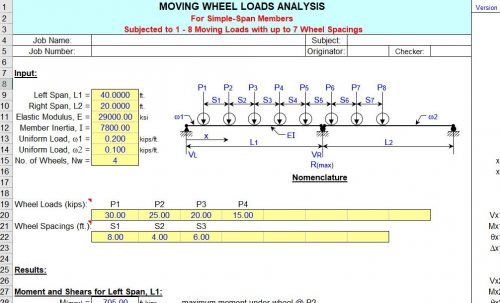
“MOVLOADS” Program
| Program Description: |
| “MOVLOADS” is a spreadsheet program written in MS-Excel for the purpose of analysis of simple-span members |
| subjected to from one (1) up to eight (8) moving wheel loads with up to seven (7) wheel spacings. Specifically, |
| the maximum moment and location from the left end of the member and wheel postioning, the maximum end |
| shears, the maximum deflection, and the maximum center support reaction for two (2) adjacent simple-span |
| members are calculated. |
| This program is a workbook consisting of two (2) worksheets, described as follows: |
| Worksheet Name |
| Doc |
| Moving Loads |
| Program Assumptions and Limitations: |
| 1. The following references were used in the development of this program (see below): |
| a. “Modern Formulas for Statics and Dynamics, A Stress-and-Strain Approach” |
| by Walter D. Pilkey and Pin Yu Chang, McGraw-Hill Book Company (1978), pages 11 to 21. |
| b. AISC 9th Edition Allowable Stress (ASD) Manual (1989), pages 2-298 and 2-310. |
| 2. This program uses the three (3) following assumptions as a basis for analysis: |
| a. Beams must be of constant cross section (E and I are constant for entire span length). |
| b. Deflections must not significantly alter the geometry of the problem. |
| c. Stress must remain within the “elastic” region. |
| 3. To determine the value of the maximum moment and location from the left end of the left span for either only one |
| (1) or two (2) wheel loads, those values are calculated directly by formulas. |
| 4. To determine the value of the maximum moment and location from the left end of the left span for three (3) up to |
| eight (8) wheel loads, the group of wheel loads is positioned with wheel load P1 situated directly over the left |
| support. Then the group is moved to the right in 1/200*span increments, and the left and right reactions as well |
| as the moments under each of the wheel loads are calculated. In moving the group of wheel loads incrementally |
| from left to right, any wheels that would drop off of the span are done so. Then this entire procedure is mirrored |
| for the opposite direction, from right to left. |
| 5. To determine the value of the maximum reaction at the center support of 2 adjacent simple spans, the group of |
| wheels is positioned with the right most wheel load situated directly over the center support. Then the group is |
| moved to the right, one wheel position at a time, until the left most wheel load, P1, is positioned directly over the |
| center support. In moving the group of wheel loads one wheel position at a time from left to right, any wheels at |
| either end that would drop off of the span(s) are done so. |
| 6. The calculated value for the maximum deflection is determined from dividing the beam into fifty (50) equal |
| segments with fifty-one (51) points, and including all of the point load locations as well. (Note: the actual point of |
| maximum deflection is where the slope = 0.) |
| 7. The user is given the ability to input two (2) specific locations from the left end of the beam to calculate the |
| shear, moment, slope, and deflection. |
| 8. This program contains “comment boxes” which contain a wide variety of information including explanations of |
| input or output items, equations used, data tables, etc. (Note: presence of a “comment box” is denoted by a |
| “red triangle” in the upper right-hand corner of a cell. Merely move the mouse pointer to the desired cell to view |
| the contents of that particular “comment box”.) |